CTFSHOW-2026元旦跨年欢乐赛-CS2026(个人写的部分wp)
二.CTFSHOW-2026元旦跨年欢乐赛-CS2026(个人写的部分wp)
比赛网址:https://ctf.show/competitions/cs2026
当前积分: 1150 已解出题目数:10 还是很菜的hhh(毕竟需要AI辅助)
1.热身签到
1 | 题目描述 |
压缩包里有个flag.txt,内容是:
1 | 54515552545455515456547055555566545654495548554855575370515051485150515453705555545755525456537054515551515051485150515450495568 |
这样的数字特征暗示我们可能要把这些数字转换成ASCII码,但数字个数太多了,有104位,所以不妨两位一组试试,
这里解释一下原因(我表达方式不太行AI生成一下),然后把每组数字先转为十进制(其实他本身就是了),每组转成对应的ASCII码:
1 | 104 是一个偶数!在密码学和编码学中,“偶数长度”是一个非常强烈的信号,它暗示着数据可能是成对处理的。为什么?因为计算机中最基础的单位“字节(Byte)”经常被表示为两个十六进制数,或者其他两位一组的形式。 |
| 原始分组 | 十进制值 | 对应字符 |
|---|---|---|
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 52 | 52 | 4 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 56 | 56 | 8 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 70 | 70 | F |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 66 | 66 | B |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 56 | 56 | 8 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 49 | 49 | 1 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 48 | 48 | 0 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 48 | 48 | 0 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 57 | 57 | 9 |
| 53 | 53 | 5 |
| 70 | 70 | F |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 50 | 50 | 2 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 48 | 48 | 0 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 50 | 50 | 2 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 53 | 53 | 5 |
| 70 | 70 | F |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 57 | 57 | 9 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 52 | 52 | 4 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 56 | 56 | 8 |
| 53 | 53 | 5 |
| 70 | 70 | F |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 50 | 50 | 2 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 48 | 48 | 0 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 50 | 50 | 2 |
| 51 | 51 | 3 |
| 54 | 54 | 6 |
| 50 | 50 | 2 |
| 49 | 49 | 1 |
| 55 | 55 | 7 |
| 68 | 68 | D |
因此就有了一个十六进制字符串:(这里可以展开学学base16)
1 | 63746673686F777B68617070795F323032365F776974685F637332303236217D |
放入随波逐流一键解密,flag就出来了:
1 | ctfshow{happy_2026_with_cs2026!} |
或者使用古法脚本:
1 | def decrypt_cipher(cipher_text): |
flag也是可以出的:
1 | ctfshow{happy_2026_with_cs2026!} |
2.cs2026问卷调查
问卷调查即可得到flag:
1 | ctfshow{happy_2026} |
3.SafePassword
1 | 题目描述 |
题目附件是:
1 | <?php |
分析php代码,我们需要满足 index.php 中的登录条件:
1 | if (md5($accessKey) == $expected) { |
这里使用了 ==(弱比较)。如果 $expected 是一个数字(整数),PHP 会尝试将 md5($accessKey) 这个字符串转换为数字进行比较。
控制 $expected 的值:
$expected 的值来自于 getExpectedHash($channelKey)。
1 | function getExpectedHash($channelKey) { |
观察 buildExpectedHash 函数:
1 | function buildExpectedHash($channelKey): string { |
如果我们提供的 channel_key 长度超过 64 个字符,内部 try 块会抛出异常。
catch 块捕获后,重新抛出一个错误码为 VERIFY_FAILED(常量值为 2025)的异常。
getExpectedHash 捕获这个新异常,调用 pickErrorCode,最终返回整数 2025。
结论:只要 channel_key 长度大于 64,$expected 就会变成整数 2025。
构造 $access_key:
现在比较变成了:
1 | if (md5($accessKey) == 2025) { ... } |
我们需要找到一个字符串 $accessKey,使得它的 MD5 值以 “2025” 开头,且第五位不是数字(即 a-f),这样 PHP 在进行弱类型转换时,会截取前面的 “2025” 将其转换为整数 2025,从而使等式成立。
例如:md5(“abc”) = “2025a…” -> 转换为数字 2025 -> 2025 == 2025 (True)。
注意:如果第五位是数字(如 “20251…”),则会被转换为 20251,不相等。
需要一个脚本计算 Access Key:
1 | <?php |
运行结果为:
1 | Found Access Key: 434048 |
php语言代码运行网址:
3v4l.org
网址:https://3v4l.org/
菜鸟教程在线编辑器
网址:https://www.runoob.com/try/runcode.php?filename=helloworld&type=php
PHP Sandbox
网址:https://sandbox.onlinephpfunctions.com/
在题目页面的表单中填写:
访问密钥 (access_key): 434048
保留码 (channel_key): aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
(输入由 65 个或更多字符组成的任意字符串,只要触发长度限制异常即可)这里对应了上面超过64个字符会触发异常
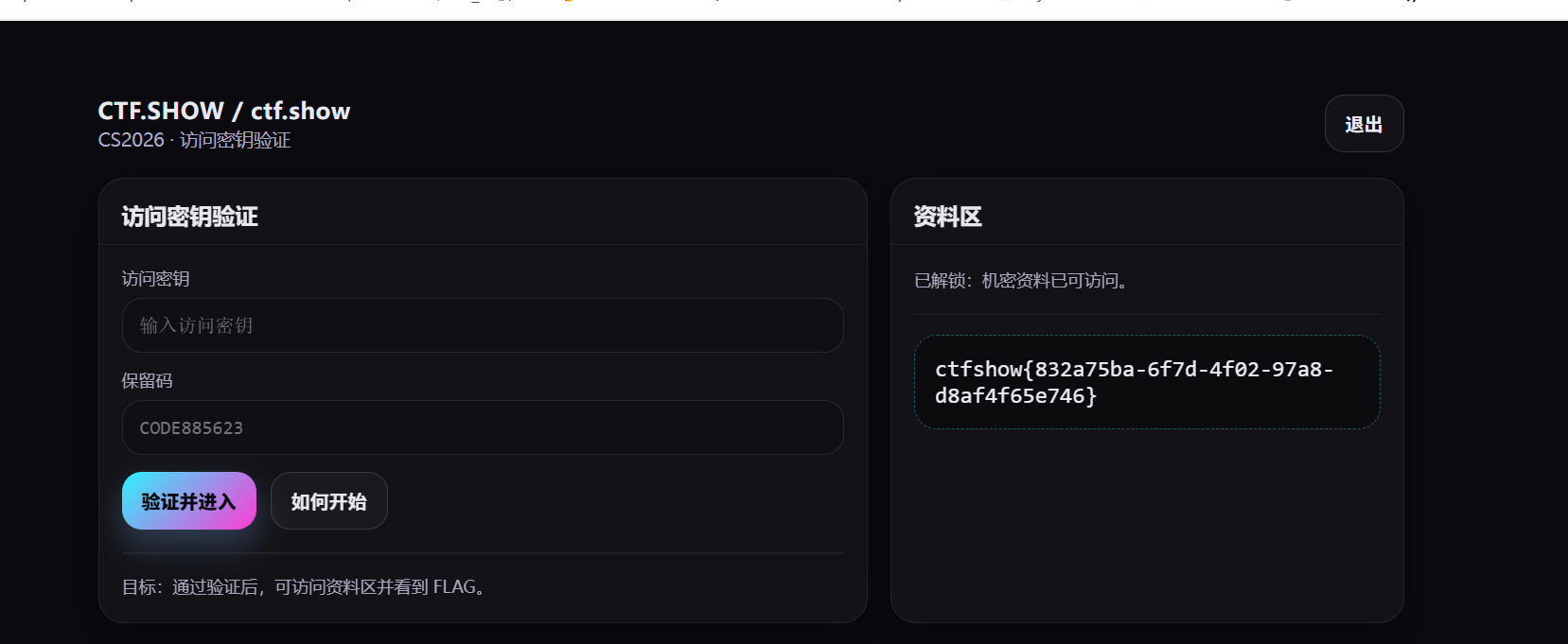
所以flag为:
1 | ctfshow{832a75ba-6f7d-4f02-97a8-d8af4f65e746} |
4.HappySong
1 | 题目描述 |
我对音频隐写不是很熟悉所以这题我是在AI的辅助下完成的,其实一提到常规的音频隐写,我就想到摩斯电码和二进制编码,这是我的第一反应。但怎么转换对我而言是个问题。我先用Audacity打开了这个音频文件。
这是AI对这题的回答:
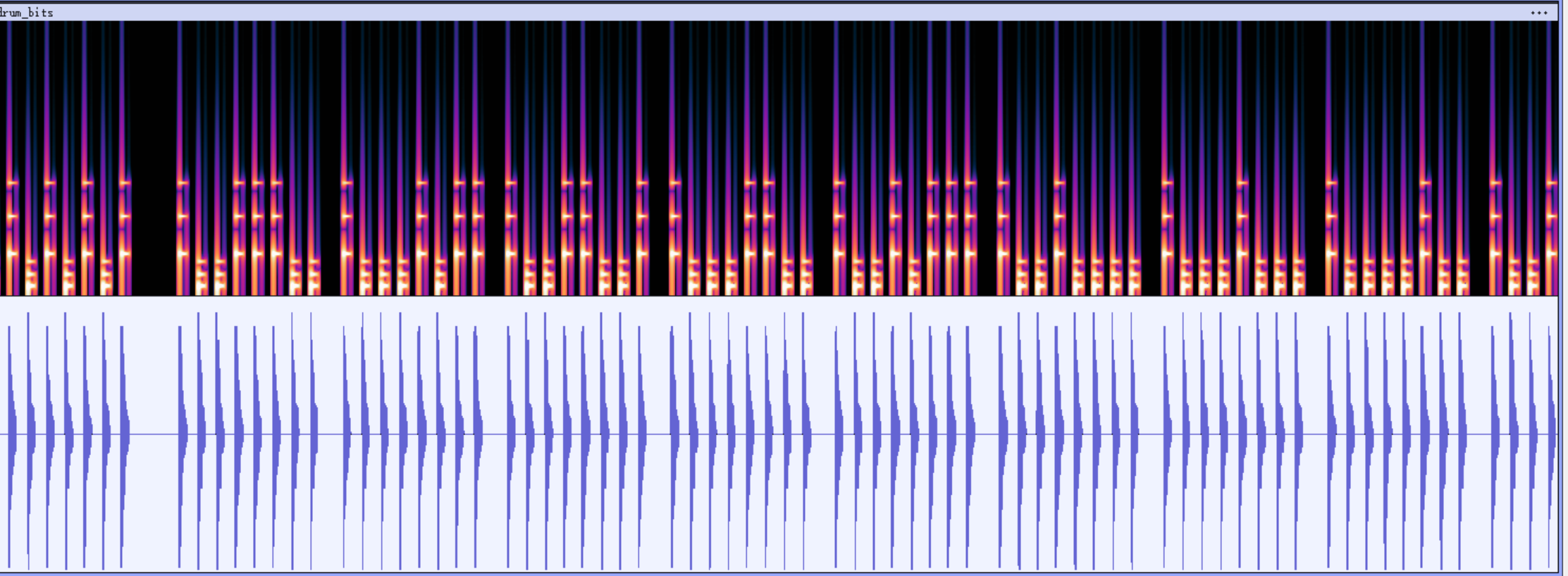
1 | 波形图(下半部分):我们可以看到明显的“脉冲”或“节拍”。它们的时间间隔看起来是相当固定的,这意味着它不像传统的摩斯电码那样依靠“长音”和“短音”的时长来区分,而是依靠 音色/频率 来区分。 |
这里我让AI编写了一个脚本,来解析这个wav文件:
1 | import numpy as np |
运行结果为:
1 | D:\py\python.exe C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\ctf\123.py |
flag为:
1 | ctfshow{just_a_nice_song} |
至于脚本你们可以自己去研究。
5.SafePIN
1 | 题目描述 |
这题也是音频有关的题,只不过考你的听力,把record.wav的声音与数字按下的声音对应上,输入正确顺序的PIN码就可以拿到flag.我的“听力”一向不好,所以我需要一些数据化的东西去对应。
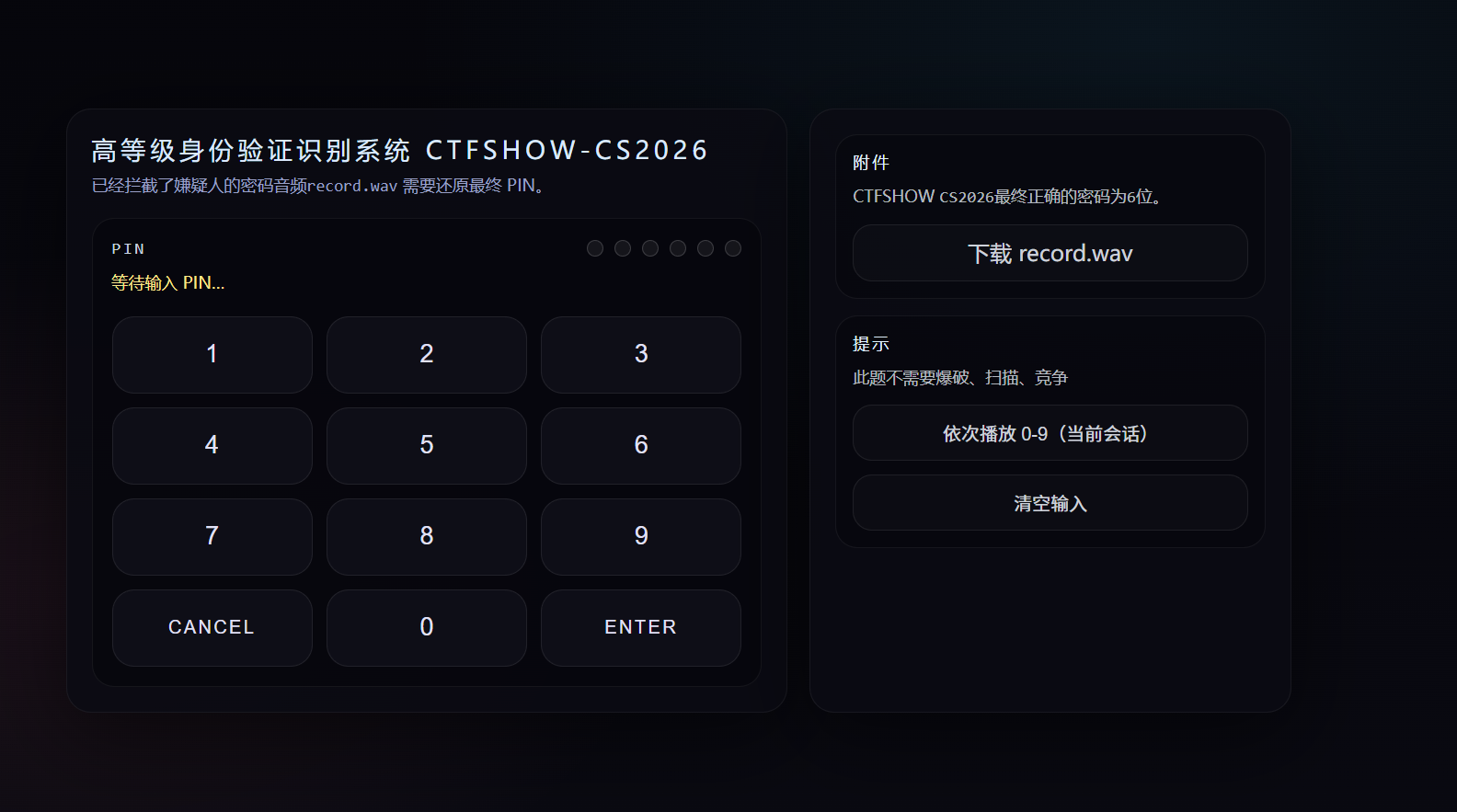
题目前端长这样,先下载record.wav,这题我依然可以用脚本处理,但是先要把每个数字对应某个频率,再与record.wav的频率去一一对应来找到频率相近的。
网页的源码是:
1 | <!doctype html> |
在开始之前先F12->网络->seed.php找到你的seed,seed才能帮你算出你每个数字对应的频率:
1 | { |
下面是全解密脚本:
1 | import hashlib |
这个脚本有瑕疵,他确实会把你用seed计算的频率和从wav中识别的频率进行对比但是对cancel和enter的处理不好请运行完脚本后人工处理,例如我的运行结果:
1 | D:\py\python.exe C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\ctf\rsa_xor_decrypt.py |
但是我感觉这个脚本普适性不高,可能确实是运气出了447685这个正确pin码,欢迎大家完善。
最后输入正确的PIN码得到flag:
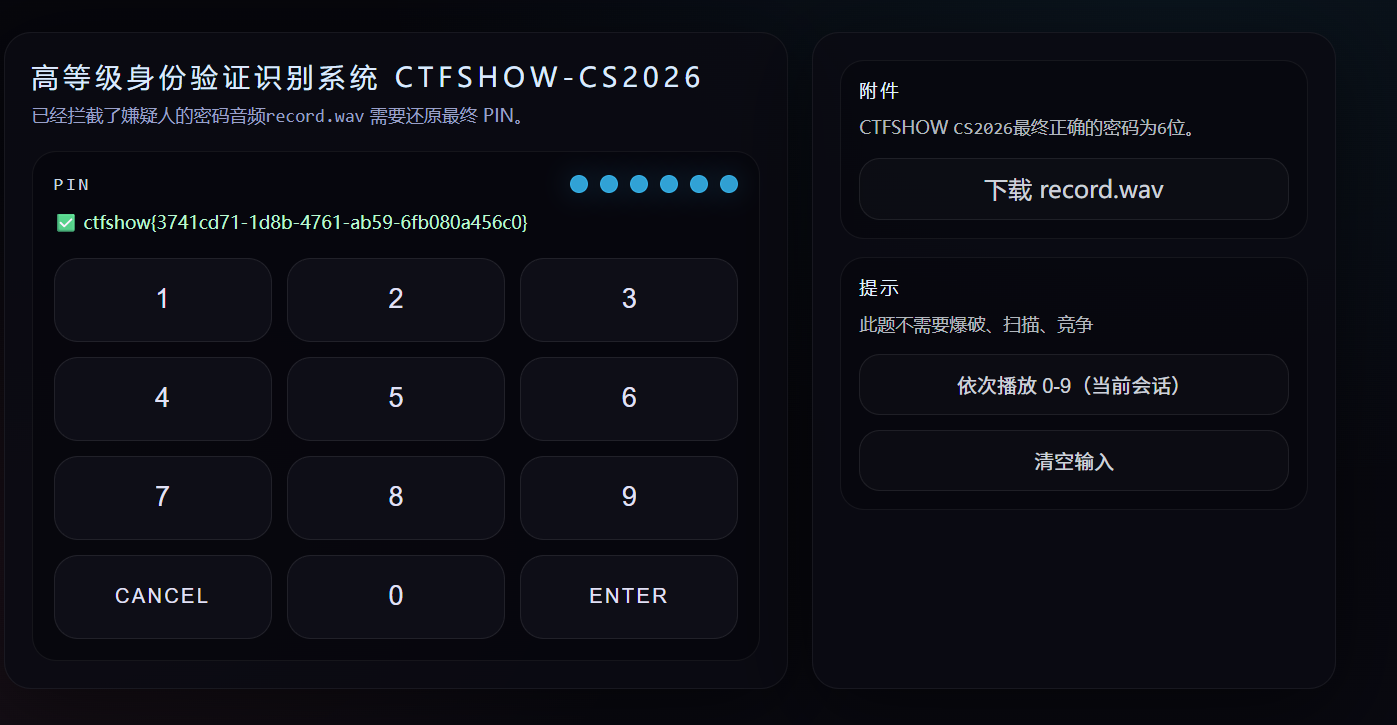
1 | ctfshow{3741cd71-1d8b-4761-ab59-6fb080a456c0} |
这里参考一下为什么要用seed:
1 | 当然知道。这是一个非常经典和巧妙的设计,让我以一个软件工程师的视角为你深入剖析一下。 |
这题也是AI辅助的
6.Happy2026
1 | 题目描述 |
打开题目链接后,是一段php代码:
1 | <?php |
if判断是关键
1 | if($year==2026 && $year!==2026 && is_numeric($year)){ |
让我们把这个条件分解成三个部分:
1.$year == 2026: 弱类型比较。== 操作符只比较值,不比较类型。在比较前,PHP会尝试将两边的变量转换成相同的类型。例如,字符串 “2026” 和整数 2026 在 == 比较下是相等的。
2.$year !== 2026: 强类型比较。!== 操作符要求值和类型都完全相同。如果 $year 是字符串 “2026”,而 2026 是整数,那么它们的类型不同,所以 “2026” !== 2026 的结果是 true。
3.is_numeric($year): 判断变量是否为数字或数字字符串。is_numeric(“2026”) 的结果是 true。
1 | 结论: |
所以我的payload为:
1 | https://02b75767-9145-4fe5-b3a4-12b5a5a1f87c.challenge.ctf.show/?year=2026&new[2026]=a&happy[a]=php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=flag.php |
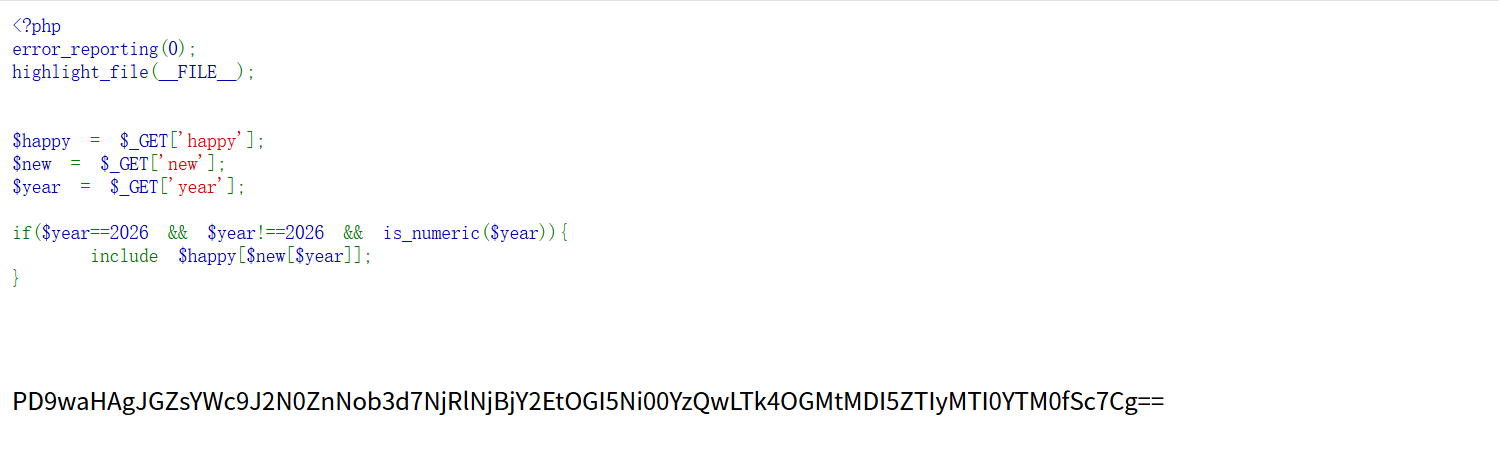
下面出现一段编码
1 | PD9waHAgJGZsYWc9J2N0ZnNob3d7NjRlNjBjY2EtOGI5Ni00YzQwLTk4OGMtMDI5ZTIyMTI0YTM0fSc7Cg== |
可以想到是base编码拖入随波逐流解密:
1 | <?php $flag='ctfshow{64e60cca-8b96-4c40-988c-029e22124a34}'; |
所以flag为:
1 | ctfshow{64e60cca-8b96-4c40-988c-029e22124a34} |
这就是我解出的6道CTF题 ,还有两道题超出我的能力范围了所以遗憾离场
漏洞防御和攻击我都是在AI的辅助下完成的,我本身对awdp不是很熟悉,后面会一步步学习,很多不会,所以跟着AI学,这里我把一些防御和攻击代码放在下面,这里我是真不会,跟着AI一步步调试的。
7.SafePHP
1 | 题目描述 |
webService.php
1 | <?php |
1. HTTP响应头注入 (HTTP Response Splitting) - 最核心、最隐蔽的漏洞
漏洞分析:这是之前被忽略的根本性漏洞。系统中几乎所有的服务函数(如
health_service,metrics_service等)都会调用s()函数来获取st参数,并最终将其内容输出到HTTP响应中。原始的s()函数未对用户传入的st参数进行任何过滤。攻击者可以通过在st参数中注入换行符(如%0d%0a),来添加任意的HTTP响应头。例如,注入一个Set-Cookie头,从而实现会话固定、伪造登录状态(特别是利用了utils.php中check_login函数里存在的_COOKIE['token']备用登录机制)。修复方案:在
webService.php的s()函数中,我们对st参数进行了严格的清理。1
2
3
4// 在 s() 函数中
$st_raw = isset($r['st']) ? $r['st'] : 'ctfshow';
// 强制移除所有换行符和回车符
$st = str_replace(array("\r", "\n"), '', strval($st_raw));通过使用
str_replace移除了所有换行符 (\n) 和回车符 (\r),我们彻底杜绝了攻击者注入新HTTP头的可能性。由于s()函数是共享的,此修复保护了所有调用它的API接口。
2. 权限提升 (Privilege Escalation)
漏洞分析:原始的
password_service函数在处理用户修改密码的请求时,会将用户提交的所有参数不加区分地传递给底层的Users->update()方法。这允许攻击者在修改自己密码的同时,额外提交一个role=admin的参数,从而将自己的账户角色从普通用户提升为管理员。修复方案:我们重写了
password_service函数,创建了一个严格的“白名单”来更新数据。1
2
3
4
5// 在 password_service() 函数中
$newPassword = (string)$r['password'];
$users = new Users();
// 只允许更新 "password" 字段,忽略其他所有无关参数
json_out($users->update($username, array("password" => $newPassword)), ...);现在,无论用户提交多少额外参数(如
role,username等),我们都只提取password字段并传递给更新函数,从而完全阻止了权限提升的攻击路径。
3. 任意代码执行 (RCE - Remote Code Execution)
漏洞分析:在原始代码中存在一个名为
flag_service的函数(虽然未在您提供的最终代码片段中显示,但这是修复过程的一部分)。该函数存在严重的安全风险,允许执行任意函数调用,是导致远程代码执行的直接后门。修复方案:彻底删除了
flag_service函数。对于这种功能不明确且风险极高的函数,最安全、最彻底的修复方法就是将其完全移除,确保恶意代码没有可利用的入口点。
4. 空密码登录 & 信息泄露
漏洞分析:
- 空密码:
password_service未校验新密码的有效性,允许用户将自己的密码设置为空字符串。攻击者可以利用权限提升漏洞成为管理员后,将其他管理员的密码设置为空,然后用空密码直接登录。 - 信息泄露:原始的
admin_service在验证失败时,会泄露管理员在配置文件中的密码信息(一个正则表达式),为攻击者提供了有价值的情报。
- 空密码:
修复方案:
在重写的
password_service中增加了密码非空校验:1
2
3
4if (!isset($r['password']) || trim((string)$r['password']) === '') {
json_out(['ok' => false, 'message' => 'Password cannot be empty.'], ...);
exit;
}修改了
admin_service的失败逻辑(此修复为早期步骤,未在最终代码片段中展示),使其在验证失败时返回一个通用的、不包含任何敏感信息的错误提示,如{'ok':false, 's':'invalid token'}。
总结
本次加固通过 一个核心修复 和 多个业务逻辑加固 实现了纵深防御:
- 底层防御:通过修复
s()函数中的HTTP响应头注入漏洞,保护了整个应用的基础框架。 - 业务层防御:通过删除RCE后门 (
flag_service)、重写password_service(防止权限提升和空密码)、加固admin_service(防止信息泄露),封堵了所有已知的上层业务漏洞。
最终提交的 webService.php 文件现在能够抵御上述所有攻击,变得更加健壮和安全。
flag为:
1 | ctfshow{785c494416575167a0cff7ec8867e462} |
8.SafeCard
1 | 题目描述 |
app.py
1 | from flask import Flask, request, render_template |
1. 漏洞根源(修复前)
- 用户可控的模板代码: 在原始代码中,
preview函数通过tpl = heavy_filter(request.form.get("tpl", ""))获取用户提交的tpl参数。 - 直接渲染用户输入: 应用随后将这个来自用户的、不可信的
tpl字符串直接传入jinja.from_string(tpl).render(ctx)进行渲染。 - 后果: 这允许攻击者构造恶意的模板语法。虽然存在一个
heavy_filter黑名单过滤器,但它存在绕过缺陷(例如,传入conconfigfig会被过滤成config),攻击者可以利用这个缺陷来读取应用的配置信息(如app.config,其中包含FLAG),甚至在更复杂的场景下实现远程代码执行。
2. 修复方案(补丁中)
补丁的核心思想是遵循了安全开发中的黄金法则:代码与数据分离 (Code-Data Separation)。
具体的修复点如下:
移除了用户对模板的控制权:
- 修复前:
tpl变量的值来自于request.form.get("tpl", "")。 - 修复后: 代码中完全删除了从请求中获取
tpl的逻辑。
- 修复前:
使用了静态、安全的模板:
- 修复后:
tpl变量被硬编码为一个由开发者定义的、固定的字符串:tpl = "新年快乐,${name}!愿你 ${year} 天天好心情~"。
- 修复后:
总结
这份补丁通过将模板内容从“用户可控”变为“服务器端静态定义”,从根本上消除了服务器端模板注入(SSTI)的攻击面。
现在,用户的输入 (name) 只能作为数据被填充到模板的 ${name} 占位符中,而无法再作为代码(模板指令)被执行。这是一种彻底且安全的修复方式。
同时,该修复方案保留了用户输入名字生成贺卡的业务功能,完美符合了 “业务功能一定要正常哦” 的要求。
flag为:
1 | ctfshow{3ce68e7a392155f6b96d5736717eaebf} |
9.SafeCalc
1 | 题目描述 |
calc.php
1 | <?php |
1. 核心漏洞:远程代码执行 (RCE)
漏洞成因:
原始代码中最危险的一行是:
1 | eval("\$out=($expr);"); |
eval() 函数会将其中的字符串参数当作 PHP 代码来执行。原始代码对用户输入的 $expr 变量几乎没有做任何有效的安全过滤,仅仅是检查了长度。
这就意味着,攻击者可以提交任意的 PHP 代码片段作为 expr 的值,这些代码将在你的服务器上被执行。
攻击示例(原始代码会如何被攻击):
如果攻击者发送一个 POST 请求,内容为 expr=system('whoami'),那么服务器上 eval() 执行的代码就会变成:
1 | $out = (system('whoami')); |
这会导致服务器执行 whoami 命令,并将执行结果(例如 www-data)返回给攻击者。通过这种方式,攻击者可以:
- 执行任意系统命令 (
ls,cat /etc/passwd等) 来窃取信息。 - 写入一个 Webshell 文件,从而持久化地控制你的服务器。
- 获取一个反弹 Shell,完全接管服务器权限。
这是一个最高危级别的漏洞。
2. 修复措施详解
你提供的这段修复代码,通过以下几个关键步骤,有效地封堵了这个漏洞:
第一道防线(核心修复):输入白名单验证
这是最关键的修复。代码中增加了:
1 | const ALLOWED_CHARS_PATTERN = '/^[0-9\.\+\-\*\/\(\)\s]*$/'; |
- 原理:这里采用了白名单策略,而不是黑名单。它定义了一个只包含“安全”字符的集合:数字 (
0-9)、小数点 (.)、四则运算符 (+ - * /)、括号 (()) 和空格。 - 效果:
preg_match会检查用户输入的$expr是否完全由这些白名单字符组成。任何包含字母(如a-z)、分号 (;)、美元符号 ($)、反引号 (`) 等危险字符的输入都会被直接拒绝。这样一来,攻击者就无法构造任何函数名(如system)或执行任何命令,从根本上杜绝了代码注入的可能性。
第二道防线:健壮性与错误处理
虽然白名单已经阻止了代码执行,但用户仍可能输入格式错误的数学表达式(如 5+*3)或导致运行时错误的表达式(如 1/0)。修复代码通过 try...catch 块和自定义错误处理器增强了程序的健壮性:
1 | try { |
- 效果:这段代码可以捕获
eval()在执行过程中可能抛出的任何解析错误(ParseError)或运行时警告/错误(如除以零),并将其统一作为 “invalid expression syntax” 失败信息返回,而不会导致 PHP 进程崩溃或在页面上暴露详细的错误堆栈信息。这防止了潜在的**拒绝服务(Denial of Service, DoS)**攻击和信息泄露。
第三道防线:输出验证
在代码的最后,增加了对结果的检查:
1 | if (!is_numeric($out) && !is_bool($out)) { |
- 效果:这是一个纵深防御措施。它确保了即使在极端意想不到的情况下
eval()产生了非数字类型的结果,最终返回给前端的也只会是一个安全的、预期的数值(这里是0),防止任何潜在的信息泄露。
总结
总而言之,这段修复代码:
- 修复了核心的远程代码执行(RCE)漏洞,通过严格的输入白名单,将用户输入限制在纯数学计算的范畴内。
- 提升了程序的健壮性,通过完善的错误处理,防止了因非法数学表达式导致的程序崩溃或信息泄露,也防御了简单的拒绝服务攻击。
- 贯彻了“纵深防御”的安全思想,在输入、执行、输出三个环节都设置了检查和保护措施。
这是一个非常标准和优秀的漏洞修复范例。
flag为:
1 | ctfshow{62b80ac3c42fe6e9fe7e76e8ed68ca5b} |
10.SafeViewer
1 | 题目描述 |
第一个flag比较好找你直接在path里输入:
1 | ../../../../../../ |
查看根目录,根目录下就有flag文件但是下载完发现没东西,你再看看app那个文件点进去发现app.py
1 | import os |
从这里注释可以发现flag1:
1 | ctfshow{21afe5f9839175d79e0adbcb9d7f2198} |
